Two popular options for permanent life insurance are Indexed Universal Life and Whole Life Insurance to maximize your wealth

Life insurance serves as a crucial financial safeguard for your family in the event of the unforeseen. If you’re seeking lifetime coverage, you’ll likely explore two permanent policy options: whole life insurance and Indexed Universal Life Both policies allow you to build cash value while providing a death benefit, but they diverge in important ways. Grasping these distinctions between Indexed Universal Life and whole life insurance can empower you to make the best choice for your needs. For comprehensive financial planning, it’s wise to engage a skilled financial advisor who can guide you through the complexities, not just in selecting the right insurance type, but in all aspects of financial decision-making.
When it comes to securing your financial future and providing for your loved ones, life insurance plays a crucial role. Two popular options for permanent life insurance are Indexed Universal Life (IUL) and Whole Life Insurance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the key differences between these two policies to help you make an informed decision that suits your financial goals.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance: An In-Depth Explanation
What is Indexed Universal Life (IUL) Insurance?
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers flexibility and potential for cash value growth. Here’s how it works: Indexed universal life insurance policies give policyholders the option to allocate all or a portion of their net premiums (after paying for the insurance coverage and expenses) to a cash account. This account credits interest based on the performance of an underlying index with a floor of 0% return and a cap rate or participation cap on the return.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance, often referred to as IUL, is a form of permanent life insurance that shares similarities with whole life insurance. IUL policies have the capability to accrue cash value over time, providing policyholders with the option to either take loans against this cash value or let it grow within the policy.
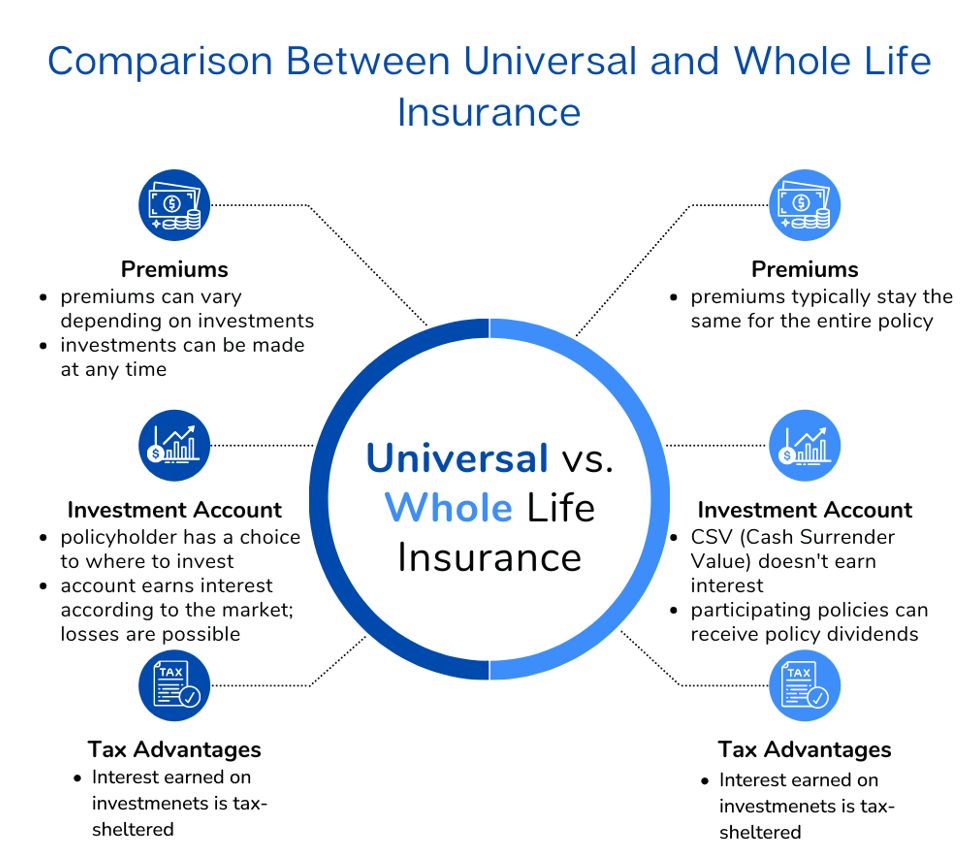
The primary distinction between whole life insurance and IUL lies in how the cash value accumulates. Whole life insurance guarantees the cash value, making the rate of return on your policy relatively predictable if you view life insurance as an investment.
On the contrary, Indexed Universal Life operates differently. The rate of return and the rate at which cash value accumulates in the policy are linked to the performance of a chosen stock market index. These indexes track specific market index or segments, such as the S&P 500 Composite Price Index or the Nasdaq.
Although indexed universal life policies can offer a higher return potential compared to whole life insurance, returns are not unlimited. Insurance companies often impose a cap rate or an annual ceiling on your returns. For example, your policy may have an annual cap rate of 3% or 4%. Additionally, insurance companies may offer a minimum guaranteed rate of return.
Advantage of Indexed Universal Life
- Guaranteed benefits
- Flexible premium payments
- Potential for higher interest earnings
- Option to borrow against policy later in life
- Interest and cash disbursements may be income-tax-free
Disadvantage of Indexed Universal Life
- Earnings depend on equity performance
- The death benefit may be reduced or forfeited if premium payments lag behind performance.
If shopping for the right life insurance policy have a wide array of choices, ranging from cheap term life insurance to expensive permanent life insurance policies.
Whole Life Insurance: An In-Depth Explanation
What is Whole Life Insurance?
Whole life insurance policies generally are considered the safest option for those looking to provide for their family after death. As such, it’s especially important to research providers to ensure they’re among the best whole insurance companies currently operating.
Whole life insurance is a permanent life insurance option that ensures lifetime coverage, contingent on the payment of premiums. Unlike term life insurance, which provides coverage for a set term (e.g., 20 or 30 years), a whole life policy offers enduring protection.
With whole life insurance, you enjoy a guaranteed death benefit that is disbursed to your beneficiaries upon your passing. Premiums typically remain consistent over time, even as the policy accrues cash value.
The accumulated cash value can be accessed through loans or employed to cover your policy’s premiums. Any outstanding loans at the time of your demise are subtracted from the death benefit bequeathed to your beneficiaries.
Advantage of Whole Life
- Guaranteed death benefits
- Fixed premiums that don’t increase with age
- Option to pay up face value in 10 years, 20 years, or at age 65
Disadvantage of Whole Life
- The interest rate may not be guaranteed (although often there will be a minimum floor rate)
- Potential opportunity cost with low relative interest rates
- Premiums aren’t flexible and must be paid consistently
The difference between indexed universal life vs whole life insurance
The main difference between whole life insurance and indexed universal life (IUL) insurance is how the cash value operates. Whole life insurance cash value grows based on a fixed interest rate. In contrast, insurance companies tie IUL cash value to a stock market index’s performance. IUL also differs from regular universal life insurance, which has a cash value that grows based on non-equity earned rates.
Indexed Universal Life (IUL) insurance and Whole Life insurance both enable you to build cash value while preserving a death benefit. However, one may align more closely with your financial objectives, contingent on your unique needs. To make an informed choice, it’s essential to understand the distinct purposes of each. Consider a Whole Life insurance policy if:
- You seek the assurance of consistent, guaranteed returns year after year.
- You prefer a guarantee that premium costs will remain stable over time.
- You want the security of a guaranteed death benefit with the option to borrow from the policy if necessary.
Whole Life insurance, while more expensive than term life insurance, is often a more cost-effective choice compared to Indexed Universal Life insurance. The assurance of guaranteed returns makes it the lower-risk alternative, appealing to those desiring a more conservative addition to their financial portfolio.
Conversely, opting for an IUL policy over Whole Life insurance offers specific benefits, such as:
- A potential for higher returns on your investment.
- Flexibility in premium payments to align with your changing financial circumstances.
- A strategy for supplementing retirement income.
It’s crucial to acknowledge that Indexed Universal Life insurance entails a degree of risk, as returns are linked to the performance of the policy’s underlying index. While there’s the potential for losses, many insurance providers offer a guaranteed minimum rate of return, limiting potential losses.
Furthermore, IUL insurance provides greater premium flexibility compared to Whole Life insurance. You may have the option to adjust your premium amount or temporarily suspend payments, with the policy’s cash value covering these expenses.
Both types of policies facilitate tax-deferred growth of the cash value, meaning you won’t incur capital gains tax on earnings unless the policy is surrendered. Additionally, any death benefits passed on to your beneficiaries remain tax-free
How to Make an Informed Choice on Life Insurance
Life insurance is a vital component of financial planning, and selecting the right policy entails careful consideration. Start by asking yourself the following key questions:
- Duration: How long do you need coverage to remain in force?
- Coverage Amount: What is the appropriate coverage level for your financial circumstances?
- Premium Comfort: How much can you comfortably allocate towards premium payments?
- Cash Value: Are you interested in building cash value within the policy?
- Risk Tolerance: To what extent are you comfortable with investment risk?
These inquiries are instrumental in determining whether a term life insurance or permanent life insurance policy is the best fit for your needs. In the case of permanent life insurance, they also aid in distinguishing between Indexed Universal Life (IUL) and Whole Life insurance.
It’s worth noting that there is a third option within permanent life insurance: variable universal life insurance. With this type, the cash value is invested directly into mutual funds or other securities, as opposed to tracking a stock market index. While it offers the highest return potential, it also carries greater investment risk.
Consulting with an insurance agent or broker is a valuable step in choosing between IUL, whole life insurance, or other life insurance types. Additionally, your financial advisor can provide guidance on how to incorporate life insurance effectively into your estate planning.
In summary, Indexed Universal Life insurance combines an investment component with life insurance, making it appealing for individuals seeking investment opportunities beyond their annual retirement contributions. Conversely, Whole Life insurance may be preferred by those desiring a guaranteed death benefit and lifelong coverage.
To gauge the appropriate life insurance coverage, you can utilize an online life insurance calculator. Generally, financial experts suggest coverage ranging from 10 to 15 times your annual income. However, your unique circumstances may necessitate a larger or smaller death benefit.
Guidelines for Determining Your Life Insurance Needs
When assessing the appropriate level of life insurance coverage, consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Identify the type of life insurance that best suits your requirements, whether it’s term life insurance or permanent life insurance.
Tip 2: Account for any existing life insurance policies you may have, including those provided by your employer.
Tip 3: Explore additional life insurance benefits, which could involve incorporating optional riders into your policy to enhance your coverage. Examples include riders for long-term care, waiver of premium, or accelerated death benefits.
Calculating Your Life Insurance Needs Manually
In addition to using a life insurance needs calculator, there are alternative methods to estimate your life insurance requirements. Here are four options:
Option 1: Multiply your annual income by 10. This is a straightforward approach for obtaining an initial estimate, but it may not fully consider factors such as outstanding debts, mortgage obligations, and future educational expenses for your children.
Option 2: Multiply your annual income by a figure greater than 10. However, this method lacks customization based on your individual circumstances, anticipated financial needs, and existing assets.
Option 3: Apply a formula of 10 times your income, plus an additional $100,000 allocated for college expenses. This approach caters to families with future college-bound children, but it may still overlook essential aspects of your unique situation.
Option 4: Employ the DIME method. The DIME method (Debt and final expenses; Income; Mortgage; Education) considers a broader range of factors than a simple income multiplier, providing a rough estimate. Nevertheless, it doesn’t account for savings or child care expenses, which are vital components in the calculation of your life insurance needs.
Wondering which life insurance policy might be right for you? Click this link to get your quote and discuss your options . Get Your Life Insurance Quote today.


















































Pingback: How to Guarantee Tax-Free Retirement Income by Investing in Life Insurance
Pingback: Infinite Banking:How to Use Life Insurance as a Source of Liquidity